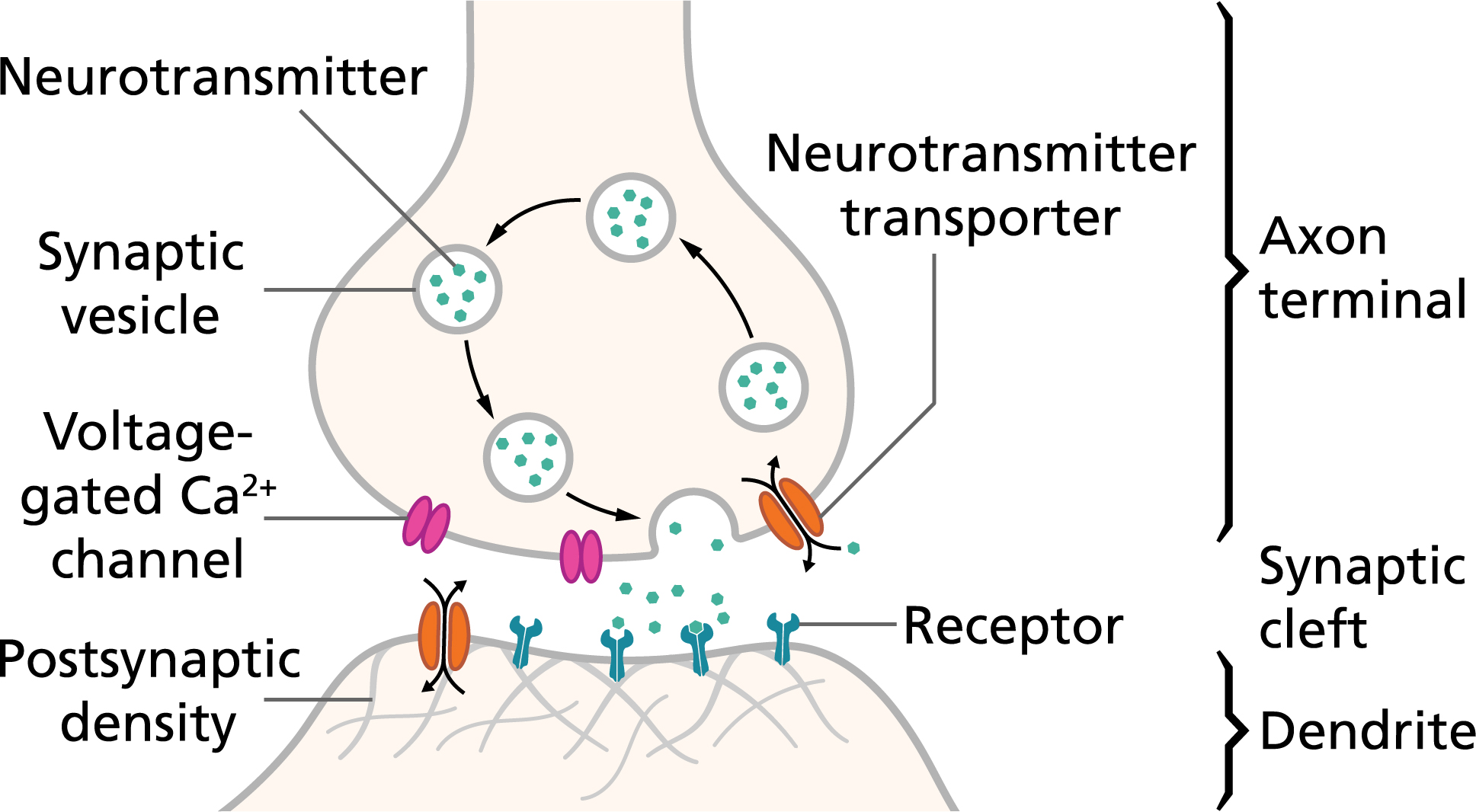
Describe the Events That Occur at a Synapse
An action potential arrives at the synapse triggering Ca2 channels to open. If youre seeing this message it means were having trouble loading external resources on our website.

Diagram Of Synaptic Transmission Okinawa Institute Of Science And Technology Graduate University Oist
Why are neurotransmitters required at chemical but not electrical synapses.

. These types of electrical synapses are very few numbers. When an impulse arrives at the end of an axon the sodium gates open and sodium floods into the axon terminal. Ca2 enters the presynaptic knob.
Calcium channels open and calcium ions flow into synaptic bulb end. This junction consists of. The influx of calcium ions into the pre-synaptic neuron as a result of the action potential reaching the synaptic end bulb.
Now the action potential generate in second neuron. This movement happens through channels called the gap junctions. A synapse forms a junction between which nerve impulses and electricity in some cases pass through a gap of approximately twenty nanometres known as the synaptic cleft from the axon terminal to the target cell.
Describe the events that take place at the synapse that enable transmission of a nerve impulse. The action potential reaches the synaptic knob at the axon terminal. This causes opening of voltage-gated Ca channels in the synaptic knob.
Describe the events that occur at a synapse starting with the arrival of the nerve signal at the synaptic knob and ending with stimulation of the postsynaptic cell. Events Occurring at a Chemical Synapse 1. When the impulse reaches the pre synaptic knob the impulse itself act as stimulus for the post synaptic neuron causing depolarization.
At the same time the calcium gates. Neurotransmitter is released by exocytosis into the synaptic cleft. In an intact brain.
Neurotransmitter binds to receptor sites on the postsynaptic neuron. The following steps are the detailed sequence of events in synaptic transmission. The neurotransmitter binds to receptors on the.
How does stimulation of the postsynaptic neuron end. It synthesizes the smaller neurotransmitters in the axon terminals and synthesizes neuropeptides in the cell body. This in turn triggers vesicles holding neurotransmitter to fuse with the presynaptic membrane releasing the neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft.
Ca rushes into the synaptic knob. Electrical synapse The presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes are locked together by gap junctions changes in transmembrane potential of one cell will produce local currents and the other cell as if they share the same membrane. Describe the events that occur at a chemical synapse when a single nerve impulse arrives at a synaptic end bulb and describe how this may lead to the initiation of a nerve impulse in the neighbouring neuron.
B When a nerve impulse reaches a synapse calcium ions enter the neurone through the pre-synaptic membrane. This causes a neurotransmitter such as acetylcholine to be released. First the neurotransmitter must be synthesized and stored in vesicles so that when an action potential arrives at the nerve ending the cell is ready to pass it along to the next neuron.
1 c Describe the role of calcium ions in synaptic transmission. Impulse transmission through synapse is accomplished by electric current. The major structural components of a synapse the site where a neuron communicates with another are a presynaptic cell and a postsynaptic cell whose plasma membranes are separated by a narrow synaptic cleft.
Briefly describe the events that occur as a cholinergic synapse. How neurons communicate with each other at synapses. An action potential occurs in the pre-synaptic neuron.
Specific ion channels open in the subsynaptic membrane. Describe and explain the sequence of events that occurs at the synapse after a neurotransmitter has been released. At the junction between two neurons an action potential causes neuron A to release a chemical neurotransmitterThe neurotransmitter can either help excite or hinder inhibit neuron B from firing its own action potential.
Action potentials travel down the axon. An action potential is propagated to the terminal of the presynaptic neuron. Nerve impulse arrives at a synaptic end bulb of the presynaptic neurons.
The process by which this information is communicated is called synaptic transmission and can be broken down into four steps. Neurons communicate with each other via electrical events called action potentials and chemical neurotransmitters. 31 is a diagram that shows the events that occur between two neurones at a synapse.
In this synapse electricity nerve impulse flows from one neuron to the other neuron due to the free movement of ions from one cell to another. The neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across synaptic cleft and bind to neurotransmitter receptors in the postsynaptic neurons plasma membrane. The release of neurotransmitters.
At the presynaptic terminal an action potential enables calcium to enter the cell. The neuron synthesizes chemicals that serve as neurotransmitters. Exocytosis of synaptic vesicles and release neurotransmitters.
Two events that occur at a synapse are. Describe the main events that will occur to complete meiosis from this stage.

Chapter 09 Muscular System Flashcards Chegg Com Muscular System Teaching Psychology Neurons
Action Potentials And Synapses Queensland Brain Institute University Of Queensland


Comments
Post a Comment